

PMID: 18295453.Ĭhris is an Intensivist and ECMO specialist at the Alfred ICU in Melbourne. Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) and facial trauma: can one size fit all? Part 4: ‘can the patient see?’ Timely diagnosis, dilemmas and pitfalls in the multiply injured, poorly responsive/unresponsive patient. Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) and facial trauma: can one size fit all? Part 3: Hypovolaemia and facial injuries in the multiply injured patient. Advanced trauma life support (ATLS) and facial trauma: can one size fit all? Part 2: ATLS, maxillofacial injuries and airway management dilemmas. Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) and facial trauma: can one size fit all? Part 1: dilemmas in the management of the multiply injured patient with coexisting facial injuries. Emergency care in facial trauma–a maxillofacial and ophthalmic perspective. Perry M, Dancey A, Mireskandari K, Oakley P, Davies S, Cameron M.Emergency department management of maxillofacial trauma. Lynham AJ, Hirst JP, Cosson JA, Chapman PJ, McEniery P.Kretlow JD, McKnight AJ, Izaddoost SA.Diagnosis and management of common maxillofacial injuries in the emergency department. Ceallaigh PO, Ekanaykaee K, Beirne CJ, Patton DW.EMCrit Podcast 112 – Exsanguinating Hemorrhage from Mid-Face Fractures (2013).Eponymictionary – René Le Fort (1869-1951).Eponymictionary – Le Fort facial fractures.internal fixation usually performed at 4-10 days once swelling has settled.prophylactic antibiotics for CSF leak are not indicated (still controversial).early surgery if orbital injury with optic nerve compression is present.open, contaminated wounds: irrigation, debridement, removal of foreign bodies and closure within 24 hours, prophylactic antiobiotics.assess and secure airway (may require cricothyroidotomy/tracheostomy).traumatic occlusion or dissection of internal carotid artery or vertebral artery.carotid-cavernous fistula (pulsatile exophthalmos, orbital bruit).CSF rhinorrhoea (anterior or middle fossa BOS #).evolving oedema over 24-48 hours can be massive and potentially threaten airway patency.prime concerns are epistaxis and septal haematoma.blow out fracture occurs when pressure directly applied to eye with fracture of inferior bony structures (enophthalmos, diplopia, impaired eye movement, infraorbital hypoesthesia).oedema and ecchymosis -> subconjunctival haemorrhage and loss of vision -> ocular rupture.

#Injury le fort fracture series#
the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and orbits act as a series of compartments that progressively collapse and absorb energy protecting the brain, spinal cord and other vital structures.bilateral # can precipitate airway obstruction from posterior displacement of tongue.fractures at the vunerable points (ramus, body at level of 1st and 2nd molar).associated injuries: BOS #, TBI, cervical spine #, carotid injury.
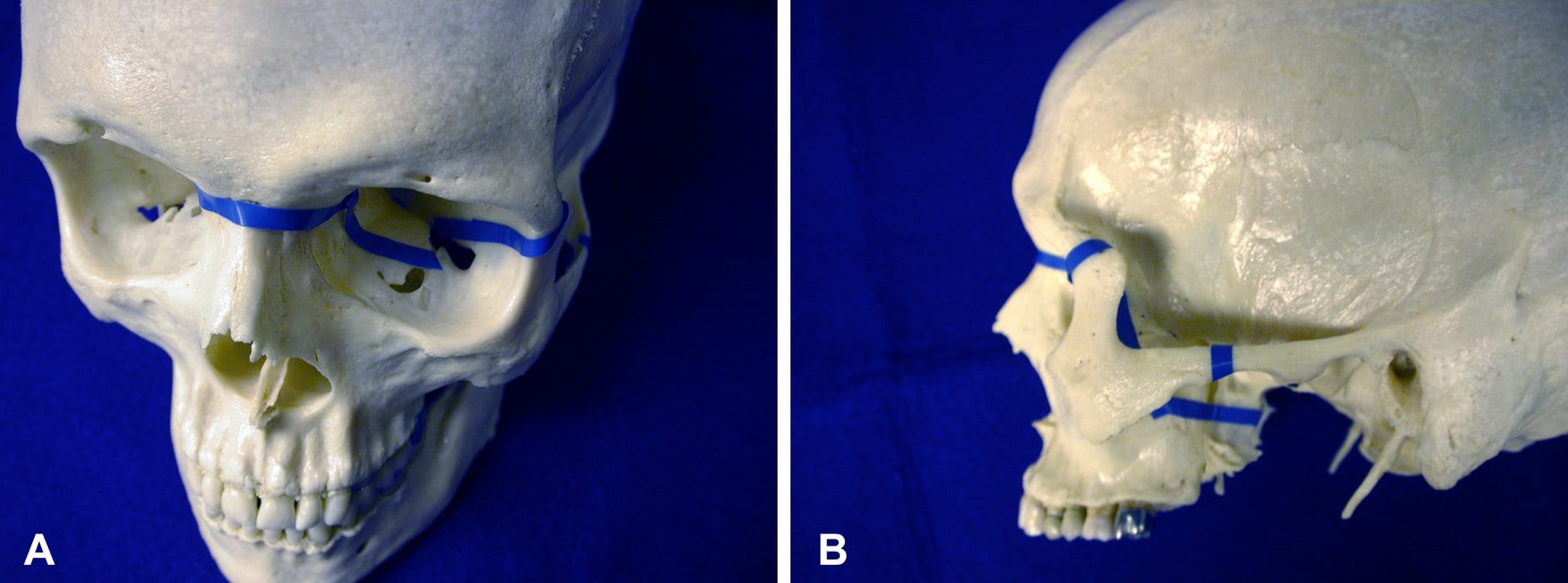
Those with facial injuries have a high chance of having other serious injuries:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
